Glossary
Some of the characteristics used to identify
your plant specimen may be unfamiliar to
you. Please familiarize yourself with the
glossary information below to assist in your
search.
Select the color that most closely resembles
the color of your plant specimen. If
your specimen has more than one color, first
search by the predominant colors. For
these reasons, try searching by other color
possibilities if your search does not yield
any species that match your specimen.
Plant Form
Herb: a seed bearing plant that lacks a
persistent woody stem.
Shrub: a woody plant
with several main stems rising at or near the ground.
Tree: a woody plant with a main and usually solitary
trunk with lateral branches.
Vine:
a herbaceous or woody plant that climbs by twining
or tendrils or that creeps along a surface.
Graminoid: grasses and other "grass-like" plants that belong to the taxonomic class called the monocots (Monocotyledoneae). Graminoids include plants of the family Poaceae or true grasses, Cyperaceae or sedges, and Juncacea or rushes.
Leaf Type
Simple: made of a single part, unbranched.
Compound: made of two or more similar and united parts, or divided into two or more similar parts or leaflets.
 Simple Alternate
Simple Alternate
 Simple Alternate
Simple Alternate
 Simple Opposite
Simple Opposite
 Simple Opposite
Simple Opposite
 Simple Whorled
Simple Whorled
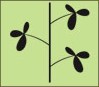 Compound Alternate
Compound Alternate
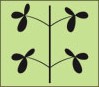 Compound Opposite
Compound Opposite
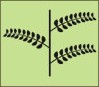 Compound Alternate
Compound Alternate
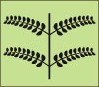 Compound Opposite
Compound Opposite
 Double Compound Alternate
Double Compound Alternate
 Double Compound Opposite
Double Compound Opposite
Leaf Arrangement
Alternate: a single leaf at a node.
Opposite: two leaves at a single node.
Whorled: three or more leaves at a single node.
 Alternate Simple
Alternate Simple
 Alternate Simple
Alternate Simple
 Alternate Compound
Alternate Compound
 Alternate Compound
Alternate Compound
 Alternate Double Compound
Alternate Double Compound
 Opposite Simple
Opposite Simple
 Opposite Simple
Opposite Simple
 Opposite Compound
Opposite Compound
 Opposite Compound
Opposite Compound
 Opposite Double Compound
Opposite Double Compound
 Whorled
Whorled
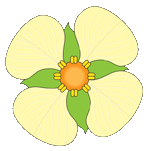
Monocots and Dicots
Flowering plants or Angiosperms are the largest and most diverse group of plants. Angiosperms are divided into Monocots and Dicots. Monocots have one seed leaf and Dicots have 2 seed leaves.
Monocots: Can be determined by:
Flower parts (sepals, petals, stamens) usually in multiples of 3's.
Major leaf veins usually in parallel arrangement.
Dicots: Can be determined by:
Flower parts usually in multiples of 4's or 5's.
Major leaf veins usually in netted or reticulated arrangement.